Isonas,
a British company, announced that in collaboration with Fujitsu and
Tolven companies it had developed the world's first wireless medical
monitoring system based on cloud computing, compliant with the guidelines of the European Medical Device Directive (MDD).
The system consists of network procedures for recording and analysis of medical data and certified sensor LifeTouch HRV011 continuously measuring five vital parameters and providing them wirelessly in real-time: Heart Rate (HR), Respiration Rate (RR), Blood Pressure (BP), Pulse Oximetry (SpO2), and Temperature (T). Other sensors can be easily added to the network.
The system can be used both for large groups,
for example, all residents of a city, and in some hospitals. Currently,
practical tests are conducted on a group of hospital patients in the
Netherlands, the system will soon be testes in the UK and India.
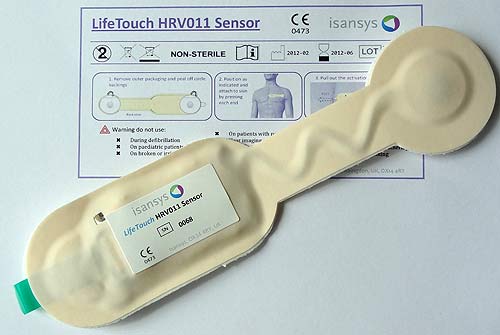
The LifeTouch HRV011 sensor is one of the elements of the certified wireless medical care system based on cloud computing
source: www.isonas.com
New
developments associated with remote medical care are also visible in
the U.S.A. In May, the FCC (Federal Communications Commission, agency
that regulates the rules for the use of radio frequencies in
communication), approved the technical studies on the assignment of
radio spectrum for wireless monitoring of patients. The spectrum for
MBAN (Medical Body Area Network) will be allocated between 2.360-2.400
MHz. The final approval of the standard is planned for 2013.
The
new technologies have to incorporate two principles: to provide the
patient with basic medical supervision at the appropriate level and
reduce the costs, compared to conventional systems. Additionally,
through online monitoring and analysis of the data doctors can
immediately react to potential threats to the patients.
1 comment:
Nice! I really enjoyed reading your post. Thanks for sharing and keep up the good work.
Post a Comment